Navigation
- Skills Learned
- Describe the benefits and usage of Cosmos DB, Azure SQL Database, Azure Database for MySQL, Azure Database for PostgreSQL, and SQL Managed Instance
- Study Guide
- Expand your knowledge - extra resources
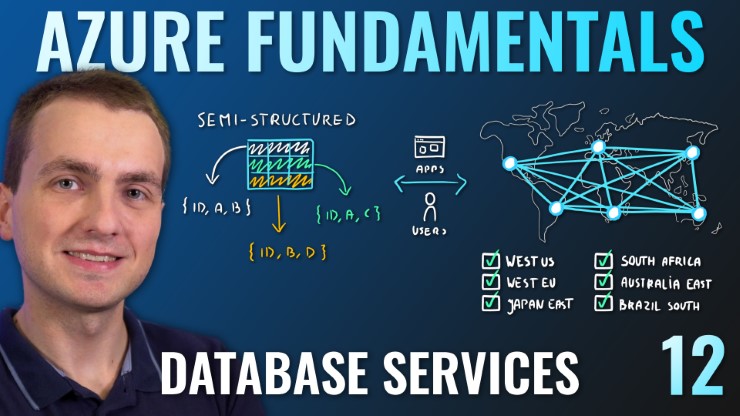
Data Types
- Structured - Data that can be represented using tables with very strict schema. Each row must follow defined schema. Some tables have defined relationships between them. Typically used in relational databases.
- Semi-structured - Data that can be represented using tables but without strict defined schema. Rows must only have unique key identifier.
- Unstructured - Any files in any format. Like binary files, application files, images, movies, etc.
Cosmos DB
- Globally distributed NoSQL (semi-structured data) Database service
- Schema-less
- Multiple APIs (SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Gremlin, Table Storage)
- Designed for
- Highly responsive (real time) applications with super low latency responses <10ms
- Multi-regional applications
SQL Database
- Relational database service in the cloud (PaaS) (DBaaS - Database as a Service)
- Structured data service defined using schema and relationships
- Rich Query Capabilities (SQL)
- High-performance, reliable, fully managed and secure database for building - applications
Azure SQL product family
- Azure SQL Database – Reliable relational database based on SQL Server
- Azure Database for MySQL – Azure SQL version for MySQL database engine
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL – Azure SQL version for PostgreSQL database engine
- Azure SQL Managed Instance – Fully fledged SQL Server managed by cloud provider
- Azure SQL on VM – Fully fledged SQL Server on IaaS
- Azure SQL DW (Synapse) – Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) version of SQL Server