Navigation
Skills Learned
- Skills Learned
- Describe products available for Storage such as Blob Storage, File Storage, Queue Storage, Table Storage, Disk Storage, and Storage Tiers
- Study Guide
- Microsoft Learn: Benefits of using Azure to store data
- Microsoft Learn: Storage Services
- Microsoft Azure: Storage Services Overview
- Microsoft Azure: Storage Services Documentation
- Microsoft Azure: Blob Storage Overview
- Microsoft Azure: Files Overview
- Microsoft Azure: Disk Storage Overview
- Microsoft Azure: Table Storage Overview
- Microsoft Azure: Queue Storage Overview
- Expand your knowledge - extra resources
- Azure Storage Tutorial | Introduction to Blob, Queue, Table & File Share
- Azure Queue Storage Tutorial
- Azure Table Storage Tutorial | Easy and scalable NoSQL database
- Azure Files Tutorial | Easy file shares in the cloud
- Azure Data Lake Storage (Gen 2) Tutorial | Best storage solution for big data analytics in Azure
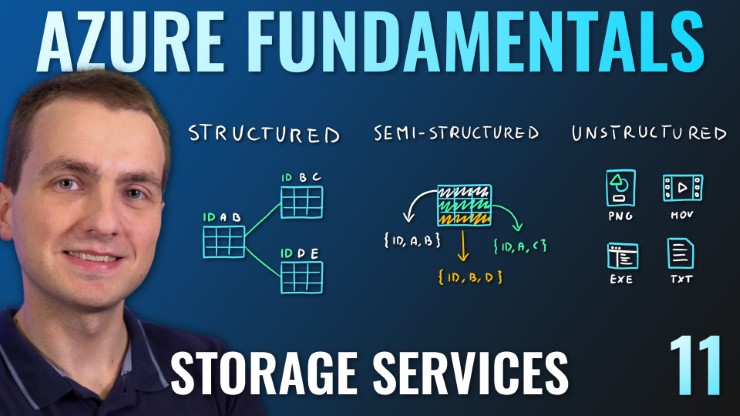
Data Types
- Structured - Data that can be represented using tables with very strict schema. Each row must follow defined schema. Some tables have defined relationships between them. Typically used in relational databases.
- Semi-structured - Data that can be represented using tables but without strict defined schema. Rows must only have unique key identifier.
- Unstructured - Any files in any format. Like binary files, application files, images, movies, etc.
Storage Account
- Group of services which include
- blob storage,
- queue storage,
- table storage, and
- file storage
- Used to store
- files,
- messages, and
- semi-structured data
- Highly scalable (up to petabytes of data)
- Highly durable (99.999999999% - 11 nines, up to 16 nines)
- Cheapest per GB storage
Blob Storage
- BLOB – binary large object – file
- Designed for storage of files of any kind
- Three storage tiers
- Hot – frequently accessed data
- Cool – infrequently accessed data (lower availability, high durability)
- Archive – rarely (if-ever) accessed data
Queue Storage
- Storage for small pieces of data (messages)
- Designed for scalable asynchronous processing
Table Storage
- Storage for semi-structured data (NoSQL)
- No need for foreign joins, foreign keys, relationships or strict schema
- Designed for fast access
- Many programming interfaces and SDKs
File Storage
- Storage for files accessed via shared drive protocols
- Designed to extend on-premise file shares or implement lift-and-shift scenarios
Disk Storage
- Disk emulation in the cloud
- Persistent storage for Virtual Machines
- Different
- sizes,
- types (SSD, HDD)
- performance tiers
- Disk can be unmanaged or managed